Tonight, as you contemplate the stars, think about the way our local star, the sun, moves through our Milky Way galaxy. A friend from Australia wrote:
I seek to find out what speed our sun is traveling at and also how many years it takes to circumnavigate the galaxy.
Our Milky Way galaxy is a collection of several hundred billion stars. It has an estimated diameter of 100,000 light-years. Our sun does indeed circumnavigate the Milky Way galaxy. In space, everything moves. There are various estimates for the speed the sun travels through the galaxy, but its speed is about 140 miles per second.
Likewise, there are many estimates for the length of time it takes the sun to complete one c..., but a typical estimate is about 230 million years.
That period of time – the length of the sun’s orbit around the Milky Way’s center – is known as acosmic year.
It so happens that astronomers know which star the sun is moving toward in its journey around the galaxy. Our sun and family of planets travel more or less toward the star Vega – and away from the star Sirius. Unsurprisingly, Vega and Sirius lie in opposite directions in Earth’s sky.
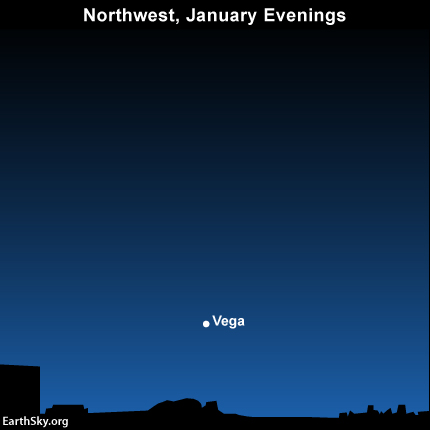
At this time of year from mid-northern latitudes, Vega star appears over the northwest horizon at dusk and early evening. Vega sets around mid-evening. It also appears low in the northeast sky in the predawn and dawn hours. It’s one of the loveliest stars you’ll ever see, Vega in the constellation Lyra the Harp.
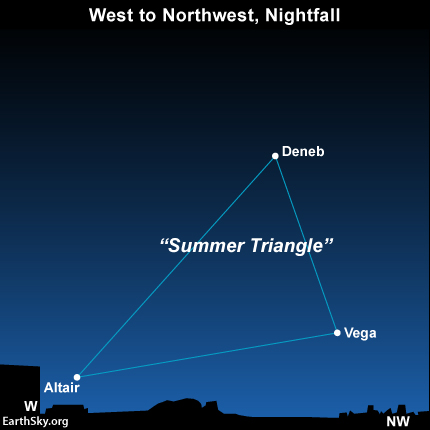
Vega is the brightest star in a famous star pattern known as the Summer Triangle. From mid-northern latitudes, as darkness falls on January evenings, the Summer Triangle sits close to the west-northwestern horizon.
Vega resides almost exactly opposite of Sirius, the brightest star in the nighttime sky. If you have an unobstructed horizon, you may see Sirius low in the southeast, as Vega sits low in the northwest.
At mid-northern latitudes, you’ll possibly see both stars around 7 to 8 p.m. local time. Sirius swings low in the southwest sky by around 3 to 4 a.m., at which time Vega reappears in the northeast sky (at mid-northern latitudes). Click here to find out when these two stars rise/set in your sky.
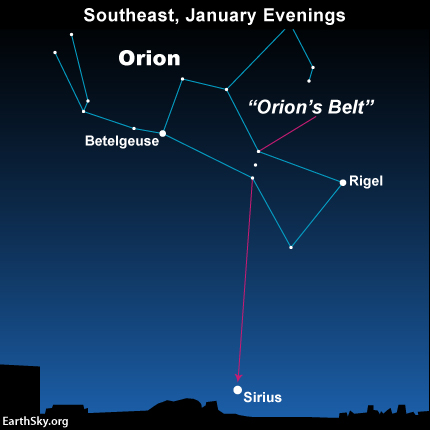
Use Orion’s Belt to find Sirius, the brightest star of the nighttime sky. From mid-latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere, you might see Sirius low in the southeast, as Vega sits low in the northwest.
Our sun’s direction of motion (and thus our Earth’s corresponding motion) toward Vega has a special name. It’s called the apex of the sun’s way. Vega – the solar apex star – can be found in the eastern sky during the dawn and predawn hours throughout the winter season.
Bottom line: Our sun moves toward the star Vega as it revolves around the center of the Milky Way galaxy. One circuit takes about 230 million years, or one “cosmic year.”
Read more about Vega: Blue-white Harp Star
A planisphere is virtually indispensable for beginning stargazers. ...
